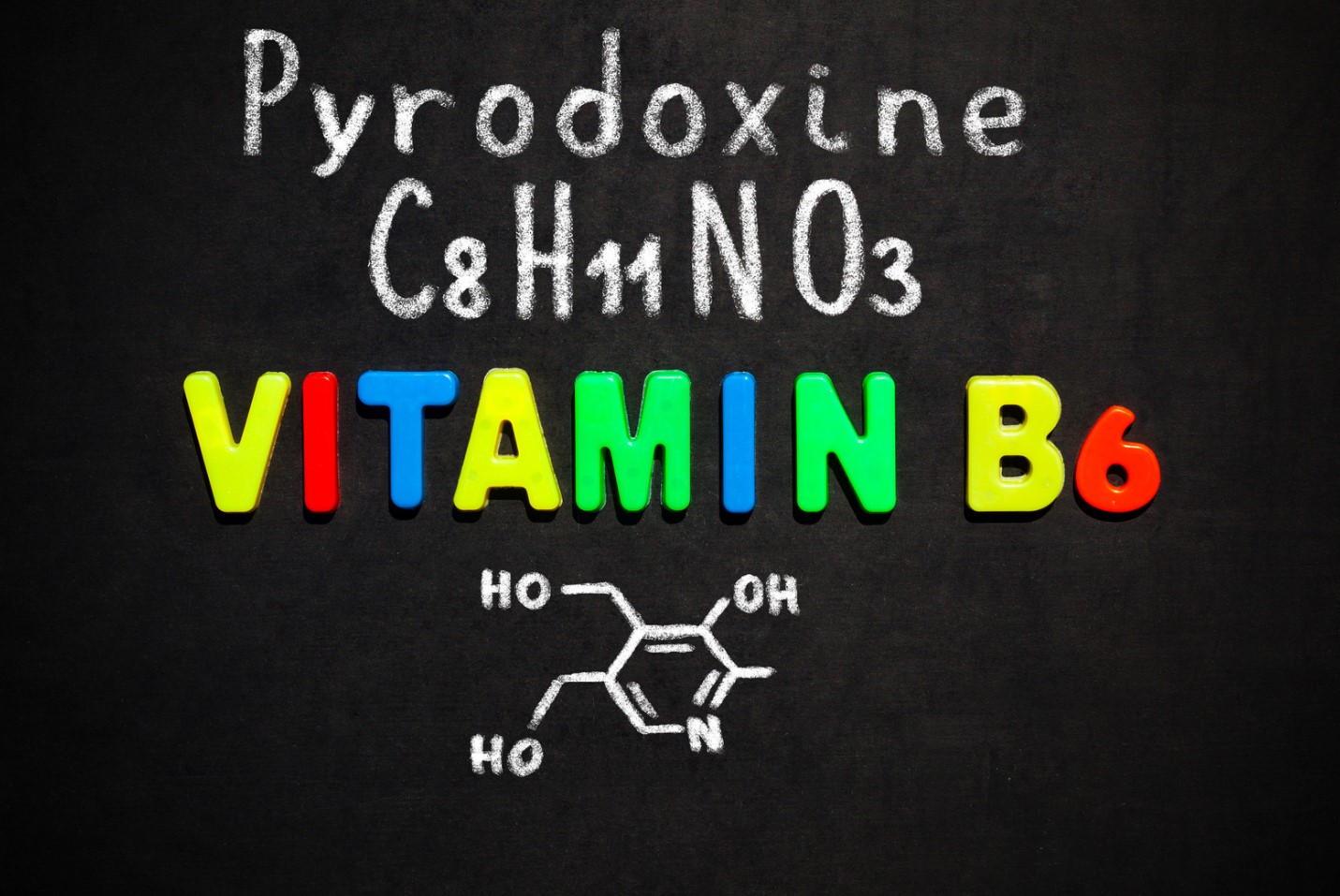
The Basics Of Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining good health. It is one of the eight B vitamins and is essential for the proper functioning of the body.
Vitamin B6 has many important functions in the body, including the conversion of food into energy, the production of red blood cells, and the support of the immune system. It is also necessary for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit messages between nerve cells.
The benefits of consuming vitamin B6 are numerous. It can help reduce inflammation, improve brain function, and promote heart health. Additionally, it has been shown to help alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and morning sickness in pregnant women.
- Vitamin B6 is required in different amounts depending on age and gender. Adult men and women require approximately 1.3mg per day.
- Foods that are high in vitamin B6 include poultry, fish, potatoes, and bananas.
- Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to a variety of symptoms, including anemia, depression, and neurological problems. People who are at risk for deficiency include those who have a poor diet, drink excessive amounts of alcohol, or who take certain medications.
In conclusion, vitamin B6 is an important nutrient that supports overall health and wellness. By incorporating foods that are high in vitamin B6 and/or taking a supplement, individuals can ensure that they are meeting their daily requirements.
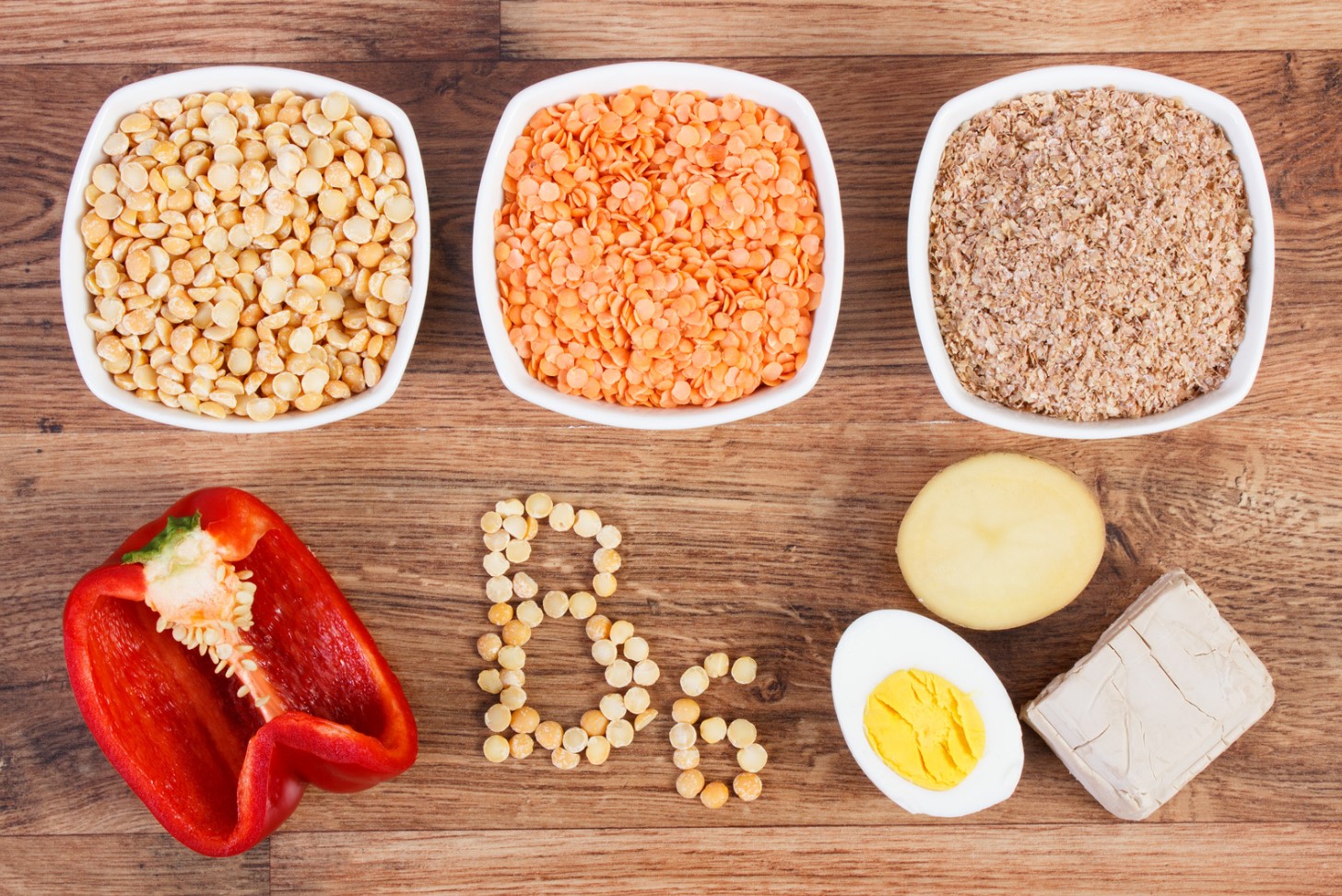
Important Functions Of Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as Pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in various bodily functions. It is a part of the B-vitamin family and helps in the conversion of food into energy. The human body cannot produce Vitamin B6, and hence it needs to be consumed through food or supplements. Here are some important functions of Vitamin B6:
- Helps in the production of neurotransmitters: Vitamin B6 is involved in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating mood, behavior, and cognitive function.
- Aids in the formation of red blood cells: Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. Hemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
- Supports the immune system: Vitamin B6 helps in the production of antibodies, which are essential for fighting off infections and diseases. It also supports the proper functioning of the immune system by aiding in the growth and maintenance of immune cells.
In addition to these functions, Vitamin B6 also helps in the production of hormones and supports the metabolism of amino acids. It is also known to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help in the prevention of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Now that we know the important functions of Vitamin B6, it is essential to understand how much of it is required daily. The recommended Daily Value for Vitamin B6 is 1.7 mg for adult men and women. Pregnant and lactating women may require more, depending on their individual needs.
| Food sources of Vitamin B6 | Vitamin B6 content (mg/serving) |
|---|---|
| Turkey breast, cooked | 0.7 |
| Salmon, cooked | 0.5 |
| Potatoes, boiled | 0.4 |
| Bananas | 0.4 |
| Spinach, cooked | 0.4 |
Some of the food sources that are high in Vitamin B6 include turkey breast, salmon, potatoes, bananas, and spinach. An individual can easily incorporate more Vitamin B6 into their diet by consuming these foods or by taking Vitamin B6 supplements, but it is always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
In conclusion, Vitamin B6 is a vital nutrient that plays several essential functions in the body. It is involved in the production of neurotransmitters, aids in the formation of red blood cells, and supports the immune system. By consuming a diet that is rich in Vitamin B6, individuals can ensure that they are getting enough of this essential nutrient to maintain optimal health.
The Benefits Of Consuming Vitamin B6
Consuming good nutrition is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Among the various essential vitamins, Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin that is necessary for the proper functioning of the body. It helps in the metabolism of protein, fats and carbohydrates, and helps to produce serotonin and norepinephrine. Vitamin B6 also plays an important role in maintaining healthy brain function and hormone regulation.
The benefits of consuming Vitamin B6 are numerous. One of the most important ways that Vitamin B6 helps the body is by aiding in the release of glycogen, which is the stored form of glucose, the body’s primary source of energy. This is particularly important for athletes and individuals with an active lifestyle.
- This vitamin also plays a significant role in preventing chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke. It does this by reducing levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that can damage blood vessels.
- Vitamin B6 also supports the immune system by producing antibodies that help fight off infections and viruses.
- Studies have shown that Vitamin B6 may also improve brain function and reduce the risk of cognitive decline in elderly individuals.
It is important to incorporate foods rich in Vitamin B6 into your diet. Some of the best food sources of Vitamin B6 include poultry, fish, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. It is recommended that adult men and women consume between 1.3 and 1.7 milligrams of Vitamin B6 daily.
| Foods High In Vitamin B6 | Vitamin B6 Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Chickpeas (1 cup) | 1.1 mg |
| Tuna (3 ounces) | 0.9 mg |
| Salmon (3 ounces) | 0.7 mg |
| Potatoes (1 medium) | 0.7 mg |
| Chicken breast (3 ounces) | 0.5 mg |
In conclusion, consuming Vitamin B6 is important for maintaining overall good health. It plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the body, including brain function, hormone regulation, and immune system support. Incorporating foods rich in Vitamin B6 into your diet is a simple and effective way to ensure that you are meeting your daily vitamin requirements.

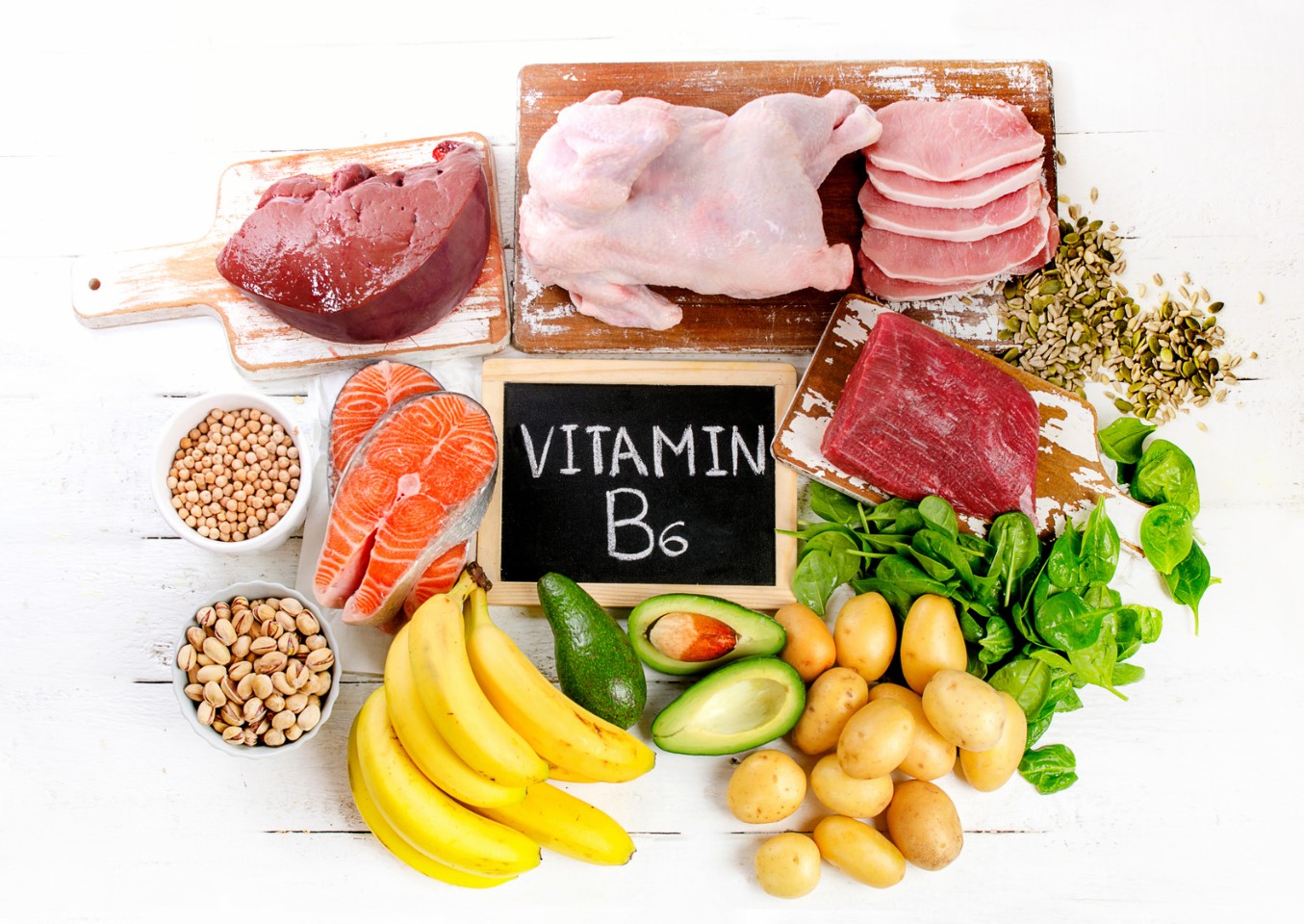
How Much Vitamin B6 İs Required Daily?
Vitamin B6, also known as Pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient that our body needs to function properly. It’s a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. As it’s a water-soluble vitamin, our body doesn’t store it, and we need to take it from external sources. How much of this vitamin do we need on a daily basis? Let’s take a look.
An average adult should intake 1.3-1.7 milligrams of vitamin B6 every day. However, if you’re pregnant, you should up this a bit, to 1.9 milligrams daily. For lactating women, it’s suggested to have 2.0 milligrams every day. It may vary according to your individual needs, and your doctor can advise you better on the recommended dosage.
Getting enough vitamin B6 is crucial for maintaining a healthy body. It has several health benefits, including maintaining healthy brain function, supporting the immune system, regulating hormonal activity, and many more. Although the recommended daily dosage may vary individually, maintaining the suggested dosage can contribute immensely to your overall health in the long run.
- Eggs
- Fortified Cereal
- Chicken Breast
- Potatoes
- Bananas
- Chickpeas
- Tuna
If you’re looking to up your vitamin B6 intake, incorporating foods that are high in vitamin B6 into your diet could help. Some of the foods that are rich in vitamin B6 include:
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | %DV | |
| Salmon (3 oz) | 0.6 | 30% |
| Chicken Breast (3 oz) | 0.5 | 25% |
| Potato, boiled (1 medium) | 0.4 | 20% |
| Banana (1 medium) | 0.4 | 20% |
| Spinach (1/2 cup) | 0.1 | 5% |
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to several health problems, such as skin disorders, mood changes, muscle pains, and in some extreme cases, anemia. Although overdosing on vitamin B6 is rare, it’s also important not to exceed the recommended dosage. Too much vitamin B6 intake may lead to toxicity, which can cause nerve damage.
To sum up, vitamin B6 is a crucial nutrient that is required to maintain a healthy body. If you’re maintaining a balanced diet, you may already be getting enough vitamin B6. However, if there is a deficiency or you’re looking to increase your intake, it’s always best to consult with your doctor for the recommended dosage.

Foods High İn Vitamin B6
Incorporating Vitamin B6 into your diet is crucial for good health, and foods rich in this essential vitamin should be included in your regular meal plan. The recommended daily intake for adults ranges from 1.3 to 1.7 milligrams, and consuming foods high in Vitamin B6 is an excellent way to meet this requirement.
Some of the best sources of Vitamin B6 come from whole foods, including poultry, seafood, and plant-based options. Notable foods high in this vitamin include turkey breast, tuna, salmon, chickpeas, potatoes, and bananas, to name a few. Here’s a closer look at some of the top food sources of Vitamin B6:
| Food | Vitamin B6 content per serving (in milligrams) |
|---|---|
| Chicken breast (3 oz) | 0.5 mg |
| Tuna (3 oz) | 0.9 mg |
| Salmon (3 oz) | 0.7 mg |
| Chickpeas (1 cup, cooked) | 1.1 mg |
| Potatoes (1 medium) | 0.4 mg |
| Bananas (1 medium) | 0.4 mg |
Keep in mind that cooking methods can impact the Vitamin B6 content of food. Boiling, frying, or baking for extended periods can reduce levels of the vitamin. Steaming or microwaving for short periods is recommended to preserve nutrient content.
By incorporating foods high in Vitamin B6 into your diet, you can increase your nutrient intake and support your overall health. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific dietary needs.
The Role Of Vitamin B6 İn Metabolism
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in a variety of bodily functions. One of its most vital functions is its role in metabolism. Metabolism is the process by which the body converts the food we eat into energy that our cells can use. Without adequate levels of vitamin B6, the body would struggle to break down and absorb important nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Vitamin B6 is involved in the metabolism of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Specifically, vitamin B6 helps convert the amino acid tryptophan into niacin, which is essential for a healthy nervous system, skin, and digestive system. Additionally, vitamin B6 helps the liver process proteins and produce hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
- Other important metabolic functions of vitamin B6 include:
- Assisting in the conversion of glycogen to glucose for energy
- Regulating blood glucose levels
- Synthesizing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine which regulate mood and behavior
It’s important to note that the body cannot produce vitamin B6 on its own, so it must be obtained through a healthy and balanced diet. Good food sources of vitamin B6 include fish, poultry, potatoes, bananas, chickpeas, and fortified cereals. However, it’s also possible to supplement with vitamin B6 if dietary intake is insufficient.
In conclusion, vitamin B6 is a crucial vitamin that plays an essential role in metabolism. Without it, the body would struggle to produce energy, absorb nutrients, and regulate important bodily functions. Incorporating vitamin B6-rich foods into your diet, or taking a supplement if necessary, can help support a healthy and efficient metabolism.
Vitamin B6 For Brain Health
Vitamin B6 is known for its vital role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, hormonal regulation, and immune system support. However, it is also essential for maintaining a healthy brain. The brain requires various vitamins and minerals to function well, and vitamin B6 is one of them. In this post, we will discuss the importance of vitamin B6 for brain health and how to incorporate it into your diet to keep your brain functioning optimally.
One of the primary functions of vitamin B6 in the brain is the production of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that enable communication between brain cells. Vitamin B6 helps the brain produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA that are necessary for regulating mood, motivation, and stress response.
Another critical role played by vitamin B6 in the brain is in the formation of myelin. Myelin is a fatty substance that forms a protective layer around nerve fibers, allowing them to conduct electrical impulses efficiently. Proper myelination is required for optimal brain functioning, and vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in its formation.
- Good dietary sources of vitamin B6 include:
- Bananas
- Avocadoes
- Beans and legumes
- Poultry and meats
- Fish and seafood
- Fortified breakfast cereals
Vitamin B6 intake varies depending on factors such as age, gender, and pregnancy/lactation status. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for adults is 1.3-1.7 mg/day. However, athletes, pregnant/lactating women, and individuals with certain medical conditions may require higher doses under medical supervision.
Dietary supplementation with vitamin B6 is generally safe when consumed within the recommended limits. Overdosing on vitamin B6 can lead to adverse effects such as nerve damage, numbness, and tingling in the extremities. However, such cases are rare and are mostly observed in individuals who take excessive amounts of vitamin B6 supplements regularly.
| Conditions that may benefit from vitamin B6 supplementation: |
|---|
| Anxiety and depression |
| ADHD |
| Migraine headaches |
| Memory loss and cognitive decline |
In conclusion, vitamin B6 plays a critical role in maintaining optimal brain health. Adequate intake of vitamin B6 through the diet or supplementation can help support healthy brain function and improve mood, memory, and overall cognitive performance.

Vitamin B6 And Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin B6, also known as Pyridoxine, is an essential vitamin required for various body functions, including metabolism, immune health, and nerve function. Besides, it also plays a pivotal role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Adequate intake of Vitamin B6 can lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases by regulating blood pressure, reducing homocysteine levels, and improving blood lipid profile. Therefore, it is essential to have an adequate amount of Vitamin B6 in the diet to keep our heart healthy.
Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure. High blood pressure is one of the significant causes of heart diseases. According to a study, Vitamin B6 supplement can reduce systolic blood pressure by 1.9 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 0.9 mm Hg. Moreover, Vitamin B6 also lowers blood pressure by reducing the production of angiotensin, a hormone that constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure. Therefore, incorporating Vitamin B6 in the diet can help regulate blood pressure and lower the risk of heart diseases.
Another way in which Vitamin B6 promotes cardiovascular health is by reducing the levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that damages the arterial wall and increases the risk of heart diseases. Vitamin B6 is essential in homocysteine metabolism, as it converts homocysteine into a non-toxic compound. According to a study, participants taking 10 mg/day of Vitamin B6 supplement had a 32% reduction in homocysteine levels. Therefore, meeting the daily requirement of Vitamin B6 can reduce the risk of heart diseases by lowering homocysteine levels.
Vitamin B6 also improves the lipid profile by increasing HDL cholesterol, also known as the “good” cholesterol, which protects against heart diseases. It also reduces the level of LDL cholesterol, also known as the “bad” cholesterol, which clogs arteries and increases the risk of heart diseases. Therefore, having an adequate amount of Vitamin B6 can improve the blood lipid profile, promoting cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, Vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient with various health benefits, including maintaining cardiovascular health. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure, reducing homocysteine levels, and improving lipid profile. Therefore, it is essential to have an adequate amount of Vitamin B6 in the diet to keep our heart healthy and prevent the risk of heart diseases.
Vitamin B6 And İmmune System Support
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble nutrient that is essential for many of our bodily functions. One of the most important roles of this vitamin is its ability to support our immune system. The immune system is responsible for protecting our bodies from harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which can cause diseases ranging from the common cold to more serious illnesses such as cancer.
Research has shown that vitamin B6 plays a key role in boosting our immune system by stimulating the production of white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infection and disease. This nutrient also supports the production of antibodies, which are proteins that can identify and destroy harmful pathogens.
- Some foods that are high in vitamin B6 include:
- Chickpeas
- Tuna
- Bananas
- Potatoes
- Salmon
- Chicken
- Spinach
In addition to its role in supporting the immune system, vitamin B6 also plays a crucial role in many other bodily functions, such as the metabolism, hormone regulation, and brain function. Because our bodies cannot produce vitamin B6 on their own, it is important to ensure that we are getting enough of this essential nutrient through our diets or supplements.
| Age | Recommended Daily Amount of Vitamin B6 |
|---|---|
| 0-6 months | 0.1 mg |
| 7-12 months | 0.3 mg |
| 1-3 years | 0.5 mg |
| 4-8 years | 0.6 mg |
| 9-13 years | 1.0 mg |
| 14-18 years (male) | 1.3 mg |
| 14-18 years (female) | 1.2 mg |
| 19-50 years (male) | 1.3 mg |
| 19-50 years (female) | 1.3 mg |
| 51+ years (male) | 1.7 mg |
| 51+ years (female) | 1.5 mg |
While vitamin B6 is generally safe, it is important not to exceed the recommended daily amount as too much of this vitamin can be harmful. Symptoms of vitamin B6 toxicity include nerve damage, skin lesions, and sensitivity to sunlight. It is best to obtain any necessary nutrients from a balanced diet and to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Overall, vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in supporting our immune system, metabolism, and overall health. By incorporating vitamin B6-rich foods into our diets and following the recommended daily amounts, we can help ensure that our bodies have the necessary nutrients to function properly.
Vitamin B6 İn Pregnancy And Lactation
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. One of the most important stages of life, where vitamin B6 plays a vital role, is during pregnancy and lactation. Pregnant and lactating women need extra nutrients to support their own health and the growth and development of their child. Let’s take a closer look at why vitamin B6 is so important during these stages.
Role during pregnancy: Vitamin B6 is necessary for the development of the fetal brain and nervous system. It also helps in the formation of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. In addition, it can aid in relieving morning sickness, which is a common symptom experienced by pregnant women. Vitamin B6 can also help prevent pregnancy-related complications such as pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes.
Role during lactation: Vitamin B6 is important for the production of breast milk. It helps in the metabolism of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Breast milk is rich in protein, and vitamin B6 ensures that the production of breast milk is optimized to provide essential nutrients to the baby.
- Foods rich in vitamin B6: Some of the foods that are high in vitamin B6 include meat, fish, poultry, bananas, nuts, and seeds.
- Dosage: Pregnant women need about 1.9 mg of vitamin B6 per day, and lactating women need around 2 mg per day. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage.
- Deficiency symptoms: Deficiency of vitamin B6 during pregnancy can lead to impaired fetal brain development, anemia, and pre-eclampsia. In lactating women, a deficiency can result in low milk supply and compromised infant health.
It is important to note that while vitamin B6 is beneficial during pregnancy and lactation, overdosing on this vitamin can be harmful. High doses of vitamin B6 can cause toxicity, resulting in nerve damage and other health issues. It is, therefore, advisable to consult a healthcare provider before taking any vitamin supplements.
Incorporating foods rich in vitamin B6 into your diet is a healthy way to ensure you are getting the required nutrient intake during pregnancy and lactation. A balanced diet is the key to a healthy pregnancy and can also ensure optimal health for your baby. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on nutrition during pregnancy and lactation.
Common Vitamin B6 Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin B6 is a vital nutrient that plays an important role in various bodily functions. It helps your body produce red blood cells, metabolize proteins and carbohydrates, and supports a healthy nervous system. However, despite its importance, many people fail to consume enough of it, resulting in a deficiency.
If you’re wondering whether you’re getting enough vitamin B6, it’s important to know the common deficiency symptoms. Some of the most common signs of a deficiency include:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Depression and irritability
- Inflammation and soreness of the mouth or tongue
- Poor concentration
In addition to these symptoms, a vitamin B6 deficiency can also lead to anemia, which means your body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to your tissues. This can cause shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches, and heart palpitations.
It’s important to note that vitamin B6 deficiency is relatively uncommon in developed countries, as it is found in many staple foods such as meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables. However, certain groups are at a higher risk of deficiency, such as the elderly, pregnant or lactating women, and people with medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption.
If you suspect you might be deficient in vitamin B6, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider. They can perform a blood test to determine your vitamin B6 levels and recommend dietary changes and supplements if necessary.
Vitamin B6 And Hormone Regulation
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential in many body functions, including hormone regulation. Hormones play a critical role in the health and wellbeing of an individual. Hormonal imbalance can cause an array of health issues, including depression, anxiety, irregular periods, and infertility, to mention a few. In this article, we will delve deeper into the topic of vitamin B6 and hormone regulation.
One of the primary benefits of vitamin B6 is its ability to regulate hormone production. The vitamin plays a critical role in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are vital in regulating our moods. It also regulates the production of cortisol, a hormone produced in response to stress. Cortisol helps our bodies respond to stress by increasing our energy levels; however, too much cortisol can lead to anxiety and depression.
Vitamin B6 is also essential in the regulation of sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are critical in the reproductive system, and any imbalance can lead to menstrual irregularities and fertility issues. Vitamin B6 helps regulate the balance of estrogen and progesterone in the body, reducing the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause.
- Some common vitamin B6-rich foods include:
- Chickpeas
- Poultry
- Sunflower seeds
- Salmon
- Tuna
Research has also shown that vitamin B6 can help regulate the thyroid gland, which produces hormones that regulate metabolism. A well-functioning thyroid is critical for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
It is essential to note that vitamin B6 alone cannot cure hormonal imbalances. However, incorporating foods rich in vitamin B6 in your diet can play a significant role in improving your hormonal balance. If you suspect a hormonal imbalance, we recommend visiting a healthcare professional to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
Vitamin B6 İn Preventing Chronic Diseases
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient that is important for various bodily functions. Apart from its role in metabolism and brain health, vitamin B6 is also believed to play a significant role in preventing chronic diseases. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the potential benefits of consuming vitamin B6 and how it can help in preventing chronic diseases.
What chronic diseases can vitamin B6 help prevent?
- Cardiovascular disease: Vitamin B6 helps in reducing homocysteine levels in the blood, which is a risk factor for heart disease. It also helps in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
- Cancer: Some studies have suggested that adequate intake of vitamin B6 can lower the risk of certain types of cancer, including lung and colon cancer.
- Diabetes: Vitamin B6 can help in controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Vitamin B6, along with other B vitamins, can help in reducing the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
How does vitamin B6 help in preventing chronic diseases?
Vitamin B6 has antioxidant properties, which means it helps in preventing damage to cells and tissues by neutralizing free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage DNA, proteins, and other important structures in the body. Oxidative stress is a known risk factor for chronic diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Additionally, vitamin B6 is involved in various metabolic pathways that are essential for maintaining overall health. For example, it helps in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, which are important for mood regulation and brain function. It also helps in the synthesis of hemoglobin, which is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
How much vitamin B6 is needed to prevent chronic diseases?
The recommended daily intake of vitamin B6 for adults is 1.3-1.7 mg per day. However, some experts have suggested that higher doses of vitamin B6 may be needed to prevent chronic diseases. It’s important to note that excessive intake of vitamin B6 can be harmful and lead to toxicity. Therefore, it’s recommended to get vitamin B6 from food sources and talk to your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
What are the food sources of vitamin B6?
| Food | Vitamin B6 content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Salmon (3 oz) | 0.5 |
| Tuna (3 oz) | 0.4 |
| Chicken breast (3 oz) | 0.5 |
| Potatoes (1 medium) | 0.5 |
| Bananas (1 medium) | 0.4 |
| Spinach (1 cup) | 0.4 |
Conclusion
Vitamin B6 is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in preventing chronic diseases. It helps in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease by neutralizing free radicals and supporting healthy metabolic pathways. To get enough vitamin B6, it’s important to consume a balanced diet that includes food sources like salmon, tuna, chicken, potatoes, bananas, and spinach. Always talk to your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Overdosing On Vitamin B6 – What To Know
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient required for various metabolic and physiological functions in our body. While a adequate intake of vitamin B6 is crucial for overall health and wellness, consuming more than the recommended amount can have adverse effects on our health. In this blog post, we will be discussing everything you need to know about overdosing on vitamin B6, its symptoms, and how to prevent it.
First and foremost, it is important to understand the recommended daily intake of vitamin B6. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for adults aged 19-50 years is 1.3 milligrams per day. However, consuming more than 100 mg/day of vitamin B6 from supplements or fortified foods can lead to toxicity symptoms.
- The symptoms of vitamin B6 toxicity include:
- – Numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet
- – Sensory changes
- – Clumsiness
- – Difficulty walking
- – Nausea, heartburn, and abdominal pain
If left untreated, vitamin B6 toxicity can also cause severe neurological damage. It is important to note that overdosing on vitamin B6 is rare and usually occurs when high doses are consumed through supplements.
To prevent vitamin B6 toxicity, it is important to stick to the recommended daily intake and avoid consuming more than 100 mg/day from supplements or fortified foods. If you are taking vitamin B6 supplements, make sure to follow the recommended dosage and talk to your healthcare provider if you are unsure about the appropriate intake.
In conclusion, while vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient required for various bodily functions, consuming more than the recommended amount can lead to toxicity symptoms. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of vitamin B6 toxicity and prevent overdosing by sticking to the recommended daily intake and avoiding unnecessary supplements.
How To İncorporate More Vitamin B6 İnto Your Diet
Vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient that has a range of important roles in the body, including metabolism, immune system support, and hormone regulation. While a deficiency in this vitamin can lead to a variety of health issues, consuming enough of it can help prevent chronic diseases and promote overall wellness. Here are some tips on how to incorporate more vitamin B6 into your diet.
- Include foods that are high in vitamin B6 in your meals. Some great sources of this nutrient include chicken breast, turkey, salmon, tuna, potatoes, bananas, avocados, and sunflower seeds.
- Consider taking a vitamin B6 supplement if necessary. It’s important to speak with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplements to your regimen.
- Use fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals, to increase your intake of vitamin B6. Be sure to read the label to ensure the product contains the recommended daily amount of this nutrient.
It’s important to note that consuming too much vitamin B6 can be harmful, as it can lead to nerve damage and other health complications. The recommended daily allowance for vitamin B6 varies by age and gender, with adult women needing around 1.5 mg per day and adult men needing around 1.7 mg per day.
| Food Source | Amount of Vitamin B6 (mg) |
|---|---|
| Chicken breast (cooked) | 0.5 mg per 3 ounces |
| Turkey (cooked) | 0.7 mg per 3 ounces |
| Salmon (cooked) | 0.5 mg per 3 ounces |
| Tuna (cooked) | 0.9 mg per 3 ounces |
| Potato (baked with skin) | 0.5 mg per medium potato |
| Banana | 0.4 mg per medium banana |
| Avocado | 0.4 mg per half avocado |
| Sunflower seeds (roasted) | 0.9 mg per ounce |
Incorporating more vitamin B6 into your diet can be easy and delicious. By incorporating vitamin B6-rich foods into your meals and considering a supplement if necessary, you can support your overall health and wellbeing.